Fieldset Macro functions
Note
For an overview, please see Fieldsets.
Note
The fieldset functions related to thermodynamics are documented in the Thermodynamic functions page.
- fieldset ( fieldset op fieldset )
Operation between two fieldsets. op is one of the operators below:
+ Addition
- Subtraction
* Multiplication
/ Division
^ Power
The fieldsets returned by these boolean operators are boolean fieldsets (containing only 1 where result is true, 0 where it is false) :
> Larger Than
< Smaller Than
>= Larger or Equal
<= Smaller or Equal
= Equal
<> Not Equal
In all of the above operations, a missing value in one of the input fieldsets results in a corresponding missing value in the output fieldset.
- fieldset ( fieldset op number )
- fieldset ( number op fieldset )
Operations between fieldsets and numbers. op is any of the operations defined above. A missing value in either input fieldset will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset.
- geopoints ( fieldset op geopoints )
- geopoints ( geopoints op fieldset )
Operations between fieldsets and geopoints. op is any of the operations defined above. Missing values, both in the fieldset and in the original geopoints variable result in a value of geo_missing_value.
- fieldset ( fieldset and fieldset )
- fieldset ( fieldset or fieldset )
- fieldset ( not fieldset )
Conjunction, Disjunction and Negation. Boolean operators consider all null values to be false and all non null values to be true. The fieldsets created by boolean operators are binary fieldsets (containing only 1 where result is true, 0 where it is false). For example:
a = retrieve(...) b = retrieve(...) c = a and b
creates a fieldset c with values of 1 where the corresponding values of fieldset a and fieldset b are both non zero, and 0 otherwise. For an example of the use of boolean operators, see the mask function. A missing value in either input fieldset will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset.
- fieldset ( fieldset and number )
- fieldset ( number or fieldset )
Boolean operations between fieldsets and numbers. See above. A missing value in either input fieldset will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset.
- geopoints ( fieldset and geopoints )
- geopoints ( geopoints or fieldset )
Boolean operations between fieldsets and geopoints. See above.
- fieldset ( fieldset & fieldset & ... )
- fieldset ( nil & fieldset & ... )
- fieldset ( fieldset & nil )
- fieldset merge ( fieldset,fieldset,... )
Merge several fieldsets. The output is a fieldset with as many fields as the total number of fields in all merged fieldsets. Merging with the value nil does nothing, and is used to initialise when building a fieldset from nothing.
- fieldset fieldset [ number ]
- fieldset fieldset [ number,number ]
- fieldset fieldset [ number,number,number ]
Extract a selection of fields from a fieldset. If one parameter is given, only one field is selected. If two parameters are given, the fields ranging from the first to the last index are returned. The optional third parameter represents an increment n - every nth field from the first to the last index are returned.
# copies fields 1, 5, 9, 13, 17 of x into y Y = X[1,20,4]
- fieldset fieldset [ vector ]
Extract a selection of fields from a fieldset. The vector supplied as the argument provides the set of indices to be used. For example:
# copies fields 2, 1, 3 of x into y x = |2, 1, 3| y = x[i]
- fieldset abs ( fieldset )
Returns the fieldset of the absolute value of the input fieldset at each grid point or spectral coefficient. Missing values are retained, unaltered by the calculation.
- fieldset acos ( fieldset )
- fieldset asin ( fieldset )
- fieldset atan ( fieldset )
Return the fieldset of the arc trigonometric function of the input fieldset at each grid point. Result is in radians. Missing values are retained, unaltered by the calculation.
- fieldset cos ( fieldset )
Returns the fieldset of the cosine of the input fieldset at each grid point. Input values must be in radians. Missing values are retained, unaltered by the calculation.
- number count ( fieldset )
Returns the number of fields in a fieldset.
- fieldset exp ( fieldset )
Returns the fieldset of the exponential of the input fieldset at each grid point. Missing values are retained, unaltered by the calculation.
- fieldset float ( fieldset, number)
Returns a fieldset with integer data converted into floating point data for more accurate computations. The second parameter is optional; if given it defines the number of bits used for packing the float values. If not given, the default value of 24 is used (unless function gribsetbits(number) has been called to set it).
- fieldset int ( fieldset )
Returns the fieldset of the integer part of the input fieldset at each grid point or spectral coefficient. Missing values are retained, unaltered by the calculation.
- fieldset integer ( fieldset )
Returns the fieldset of the integer part of the input fieldset at each grid point or spectral coefficient. This function modifies the resulting GRIB header to be of integer data type. Missing values are replaced with LONG_MAX. This function was used in Metview 3 to enable the plotting of certain types of satellite imagery.
- fieldset log ( fieldset )
Returns the fieldset of the natural log of the input fieldset at each grid point. Missing values are retained, unaltered by the calculation.
- fieldset log10 ( fieldset )
Returns the fieldset of the log base 10 of the input fieldset at each grid point. Missing values are retained, unaltered by the calculation.
- fieldset neg ( fieldset )
Returns the fieldset of the negative of the input fieldset at each grid point or spectral coefficient. The same as (- fieldset). Missing values are retained, unaltered by the calculation.
- fieldset sgn ( fieldset )
Returns the fieldset of the sign of the values of the input fieldset at each grid point or spectral coefficient: -1 for negative values, 1 for positive and 0 for null values. Missing values are retained, unaltered by the calculation.
- fieldset sin ( fieldset )
Returns the fieldset of the sine of the input fieldset at each grid point. Input fieldset must have values in radians. Missing values are retained, unaltered by the calculation.
- fieldset sqrt ( fieldset )
Returns the fieldset of the square root of the input fieldset at each grid point. Missing values are retained, unaltered by the calculation.
- fieldset tan ( fieldset )
Return the tangent of the input fieldset at each grid point. Input fieldset must have values in radians. Missing values are retained, unaltered by the calculation.
- number or list accumulate ( fieldset )
For each field in the fieldset, this function calculates the sum of all the values of the field. If there is only one field in the fieldset, a number is returned. Otherwise, a list of numbers is returned. Only non-missing values are considered in the calculation. If there are no valid values, the function returns nil for that field.
- number or list average ( fieldset )
For each field in the fieldset, this function calculates the average of all the field values. If there is only one field in the fieldset, a number is returned. Otherwise, a list of numbers is returned. Only non-missing values are considered in the calculation. If there are no valid values, the function returns nil for that field.
Note
averagesimply returns the mathematical average of all the field values using the following formula:\[average = \frac {1}{N} \sum_{i}^{N}f_{i}\]To get the physically correct average based on the grid cell areas use
integrate.
- vector or list average_ew ( fieldset,list,number )
The function average_ew() takes as parameters a fieldset, a list of four numbers that define an area ( [N,W,S,E] ) and a number that defines the output one-dimensional grid interval in degrees.
The function returns a vector (if the input fieldset contains only one field) or a list of vectors. The elements of the returned vector(s) are means computed over rows of similar latitude using those grid points that fall inside the given area. Means are computed at intervals as specified in the third parameter. The output vector size is thus independent of the grid interval in the input fieldset.
Each grid point value is weighted by the cosine of its latitude. Missing values are ignored. If a latitude belt contains no grid point values then the missing value indicator vector_missing_value is returned.
Example:
ave = average_ew(fs, [60,-180,-60,180], 2.5)
This function call will compute means over full latitude circles starting from 60N, stepping 2.5 degrees until 60S. If fs contains only one field the output would be a vector of 49 E-W mean values, from North to South. If fs contains n fields then the output would be a list of n vectors, where each of these n vectors would contain 49 means.
For the above example, each value returned (representing the mean at latitude Lat ) is the mean of non-missing values in those grid points whose latitude coordinate is between Lat-1.25 and Lat+1.25 (1.25 is 2.5/2), i.e. within a latitude belt with width of 2.5 degrees, centered around Lat.
- vector or list average_ns ( fieldset,list,number )
The function average_ns() takes as parameters a fieldset, a list of four numbers that define an area ( [N,W,S,E] ) and a number that defines the output one-dimensional grid interval in degrees.
The function returns a vector (if the input fieldset contains only one field) or a list of vectors. The elements of the returned list(s) are means computed over lines of similar longitude using those grid points that fall inside the given area. Means are computed at intervals as specified in the third parameter. The output vector size is thus independent of the grid interval in the input fieldset.
Each grid point value is weighted by the cosine of its latitude. Missing values are ignored. If a longitude line contains no grid point values then the missing value indicator vector_missing_value is returned.
Example:
ave = average_ns(fs, [30,0,-30,360], 5)
This function call will compute means over longitudes 30N…30S, in 5 degree intervals around the globe. The result for each field in fs would be a vector of 73 values (in this case values for 0 and 360 are duplicated values).
Each value returned (representing the mean at longitude Lon ) is a mean of non-missing values in those grid points whose longitude coordinate is between Lon-2.5 and Lon+2.5 (2.5 is 5/2), in the belt between 30N and 30S.
- fieldset bearing (f: fieldset, reflat: number, reflon: number )
- fieldset bearing (f: fieldset, ref: list )
Computes the bearing for each grid point with reference to the given location. The location (in degrees) may be specified by supplying either two numbers (latitude and longitude respectively) or a 2-element list containing latitude and longitude in that order.
The bearing is the angle between the Northward meridian going through the reference point and the great circle connecting the reference point and the given gridpoint. It is measured in degrees clockwise from North. If a gridpoint is located on the same latitude as the reference point the bearing is regarded constant: it is either 90° (East) or 270° (West). If the gridpoint is co-located with the reference point the bearing is set to a missing value.
- date or list base_date ( fieldset )
Returns the base dates (including the time components) of the given fields. If the fieldset has only one field, a date is returned; otherwise a list of dates is returned.
- fieldset bitmap (fieldset,number)
- fieldset bitmap (fieldset,fieldset)
Returns a copy of the input fieldset (first argument) with zero or more of its values replaced with grib missing value indicators. If the second argument is a number, then any value equal to that number in the input fieldset is replaced with the missing value indicator. If the second argument is another fieldset with the same number of fields as the first fieldset, then the result takes the arrangement of missing values from the second fieldset. If the second argument is another fieldset with one field, the arrangement of missing values from that field are copied into all fields of the output fieldset.
Note
See also
nobitmap.
- number or list corr_a ( fieldset,fieldset )
- number or list corr_a ( fieldset,fieldset,list )
Computes the correlation between two fieldsets over a weighted area. The area, if specified, is a list of numbers representing North, West, South, East. If the area is not specified, the whole field will be used in the calculation. The result is a number for a single field, or a list for a multi-field fieldset.
Note that the following lines are equivalent, although the first is more efficient:
z = corr_a (x, y) z = covar_a (x, y) / (sqrt(var_a(x)) * sqrt(var_a(y)))
- fieldset coslat ( fieldset )
For each field in the input fieldset, this function creates a field where each grid point has the value of the cosine of its latitude.
- fieldset covar ( fieldset,fieldset )
Computes the covariance of two fieldsets.
With N fields in the two fieldsets by denoting the i-th value in the k-th field by \(x_{i}^{k}\) and \(y_{i}^{k}\) respectively, the output values can be written as:
\[z_{i} = \frac {1}{N} \sum_{k}^{N}x_{i}^{k}y_{i}^{k} - \frac {1}{N} \sum_{k}^{N}x_{i}^{k} \frac {1}{N} \sum_{k}^{N}y_{i}^{k}\]Note that the following lines are equivalent:
z = covar(x,y) z = mean(x*y)-mean(x)*mean(y)
A missing value in either input fieldset will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset.
- number or list covar_a ( fieldset,fieldset )
- number or list covar_a ( fieldset,fieldset,list )
Computes the covariance of two fieldsets over a weighted area. The area, if specified, is a list of numbers representing North, West, South, East. If the area is not specified, the whole field will be used in the calculation. The result is a number for a single field, or a list for a multi-field fieldset.
- list datainfo ( fieldset )
Returns a list of definitions - one for each field in the fieldset. Each definition provides the following members: the index of the field in the fieldset, the number of missing values, the number of values that are present and the proportion of each. The following example illustrates how to use the function.
fs = read (strGribFile) listdefInfo = datainfo (fs) loop defInfo in listdefInfo print ("Field index : ", defInfo.index) print ("Number of values present : ", defInfo.number_present) print ("Number of values missing : ", defInfo.number_missing) print ("Proportion values present : ", defInfo.proportion_present) print ("Proportion values missing : ", defInfo.proportion_missing) end loop
- fieldset direction ( fieldset,fieldset )
Returns a fieldset with the value in each grid point being the direction computed from the given U and V fieldsets; the first input fieldset is assumed to be the East-West (U) component and the second the North-South (V) component. The resulting numbers are directions, in degrees clockwise from North, where a value of 0 represents a wind from the North and a value of 90 represents a wind from the East.
A missing value in either input fieldset will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset.
- fieldset distance ( fieldset,number,number )
- fieldset distance ( fieldset,list )
Returns a fieldset with the value in each grid point being the distance in meters from the given geographical location. The location may be specified by supplying either two numbers (latitude and longitude respectively) or a 2-element list containing latitude and longitude in that order. The location should be specified in degrees.
- fieldset div ( fieldset,fieldset )
Returns a fieldset with as many fields as the input fieldsets; the grid points of the output fieldset are the integer part of the division of the first fieldset by the second fieldset (the function operating field by field).
A missing value in either input fieldset will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset.
- fieldset divergence (fx: fieldset, fy: fieldset)
Computes the horizontal divergence of 2-dimensional vector fields. The computations for a vector field f=(fx,fy) are based on the following formula:
\[div(f) = \frac{1}{R \ cos\phi}\frac{\partial f_x}{\partial \lambda} + \frac{1}{R}\frac{\partial f_y}{\partial \phi} - \frac{f_y}{R}tan\phi\]where:
R is the radius of the Earth (in m)
\(\phi\) is the latitude
\(\lambda\) is the longitude.
The derivatives are computed with a second order finite-difference approximation. The resulting fields contain missing values on the poles. If the input fields are horizontal wind components the GRIB paramId of the resulting field is set to 155 (=divergence). Please note that this function is only implemented for regular latitude-longitude grids.
- fieldset duplicate ( fieldset,number )
Returns a fieldset with the specified number of copies of the field in the input fieldset. The input fieldset must contain only one field.
- list find ( fieldset,number )
- list find ( fieldset,number,list )
- list find ( fieldset,number,field )
A filtering function that returns a list of locations (lat/long pairs), where the values of the input fieldset given as the first argument equal the value specified as the second argument. Missing values in the input field are not returned.
if there is a third argument, and it is a list of four numbers (lat/long coordinates) defining a geographical area - [North,West,South,East] , the function returns a list of locations within that area where the fieldset values equal the input value
if there is a third argument, and it is a mask field, the function returns a list of locations within the area defined by the mask (ie, where the mask gridpoints are non-zero) where the fieldset values equal the input value.
- list find ( fieldset,list )
- list find ( fieldset,list,list )
- list find ( fieldset,list,field )
A filtering function that returns a list of locations (lat/long pairs), where the values of the input fieldset given as the first argument are within the interval [a, b] specified as the second argument (a two value list). Missing values in the input field are not returned.
if there is a third argument, and it is a list of four numbers (lat/long coordinates) defining a geographical area - [North,West,South,East] , returns a list of locations within that area where the field values are within the interval [a, b]
if there is a third argument, and it is a mask field, returns a list of locations within the area defined by the mask (ie, where the mask gridpoints are non-zero) where the fieldset values are within the interval [a, b]
- fieldset first_derivative_x (f: fieldset)
Computes the zonal (from West to East) partial derivative of each field in the fieldset. The computations for a field f are based on the following formula:
\[\frac {\partial f}{\partial x} = \frac{1}{R \ cos\phi}\frac{\partial f}{\partial \lambda}\]where:
R is the radius of the Earth
\(\phi\) is the latitude
\(\lambda\) is the longitude.
The derivatives are computed with a second order finite-difference approximation. The resulting fields contain missing values on the poles. Please note that this function is only implemented for regular latitude-longitude grids.
- fieldset first_derivative_y (f: fieldset)
Computes the meridional (from South to North) partial derivative of each field in the fieldset. The computations for a field f are based on the following formula:
\[\frac {\partial f}{\partial y} = \frac{1}{R}\frac{\partial f}{\partial \phi}\]where:
R is the radius of the Earth
\(\phi\) is the latitude
\(\lambda\) is the longitude.
The derivatives are computed with a second order finite-difference approximation. The resulting fields contain missing values on the poles. Please note that this function is only implemented for regular latitude-longitude grids.
- list frequencies ( fieldset,list )
- list frequencies ( fieldset,list,list )
Counts the number of grid points whose values fall within a set of specified intervals. These intervals are given as the second argument - a list of values in ascending order, starting with the upper bound of the first interval, eg [0, 10, 20] . A third argument, if given, specifies a geographical area over which to consider values - [North,West,South,East] . Missing values in the input field are not included in the results.
If the input fieldset has just one field, then the result is a list of n+1 elements where n is the number of elements in the interval list. Using the above example, the output list could be described as follows:
the first element is the number of values below 0
the second element is the number of values in the range [0, 10)
the third element is the number of values in the range [10, 20)
the fourth element is the number of values above 20
If the input fieldset has more than one field, the result is a list of lists, one for each field. Note that this function accumulates its results between fields in a fieldset.
- fieldset geostrophic_wind (z: fieldset)
Computes the geostrophic wind from geopotential fields defined on pressure levels. For a given z geopotential field the computation of the geostrophic wind components is based on the following formulas:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}u_g = -\frac{1}{f} \frac{1}{R}\frac{\partial z}{\partial \phi}\\v_g = \frac{1}{f} \frac{1}{R \ cos\phi}\frac{\partial z}{\partial \lambda}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]where:
R is the radius of the Earth
\(\phi\) is the latitude
\(\lambda\) is the longitude.
\(f=2\Omega sin\phi\) is the Coriolis parameter, where \(\Omega\) is the Earth’s angular velocity.
The derivatives are computed with a second order finite-difference approximation. The resulting fieldset contains two fields for each input field: the u and v geostrophic wind components. In each output field the points close to the poles and the Equator are bitmapped (they contain missing values). Please note that this function is only implemented for regular latitude-longitude grids.
- geopoints gfind ( fieldset,number )
- geopoints gfind ( fieldset,number,number )
A filtering function that returns a geopoints holding the grid points whose value is equal to the value of the first number. Missing values in the input field are not returned. If a second number is given as the third argument it is a tolerance threshold and the geopoints will hold the grid points for which:
abs(data-value) <= threshold
- fieldset gradient (f: fieldset)
Computes the horizontal gradient of each field in the fieldset. The computations for a field f are based on the following formula:
\[\nabla f = (\frac {\partial f}{\partial x}, \frac {\partial f}{\partial y}) = (\frac{1}{R \ cos\phi}\frac{\partial f}{\partial \lambda}, \frac{1}{R}\frac{\partial f}{\partial \phi} )\]where:
R is the radius of the Earth (in m)
\(\phi\) is the latitude
\(\lambda\) is the longitude.
The derivatives are computed with a second order finite-difference approximation. The resulting fieldset contains two fields for each input field: the zonal derivative followed by the meridional derivative. The output fields are bitmapped on the poles (they contain missing values there). Please note that this function is only implemented for regular latitude-longitude grids.
- list grib_get (fieldset, list, [string])
For the efficient retrieval of multiple GRIB keys from a fieldset. A single call to grib_get can replace multiple calls to the other grib_get_* functions and is hence more efficient. The keys are provided as a list for the second argument; by default they will be retrieved as strings, but their type can be specified by adding a modifier to their names, following the convention used by grib_ls where the key name is followed by a colon and then one or two characters which specify the type:
s=string
l=long
d=double
la=long array,
da=double array
n=native type New in Metview version 5.14.0
For example, the key ‘centre’ can be retrieved as a string with ‘centre’ or ‘centre:s’, or as a number with ‘centre:l’. Each GRIB key has a ‘native type’, e.g. long or string. If the type is specified as “n” then the type that is returned. The native type for the key ‘centre’ is str, so ‘centre:n’ will return a str.
The result is always a list of lists; by default, or if the optional third argument is ‘field’, the result will be grouped by field, containing one list per field, each of these lists containing one element per key; if the optional third parameter is ‘key’, the result will be grouped by key, containing one list per key, each of these lists containing one element per field. Example - the following lines of Macro code on a particular 6-field fieldset:
print(grib_get(data, ['editionNumber', 'centre', 'level', 'step'], 'field')) print(grib_get(data, ['editionNumber', 'centre:l', 'level', 'step'], 'key'))
produces this output:
[[1,ecmf,1000,0],[1,ecmf,500,0],[1,ecmf,100,0],[1,ecmf,1000,48],[1,ecmf,500,48],[1,ecmf,100,48]] [[1,1,1,1,1,1],[98,98,98,98,98,98],[1000,500,100,1000,500,100],[0,0,0,48,48,48]]
- number or list grib_get_long ( fieldset, string )
- number or list grib_get_double ( fieldset, string )
- number or list grib_get_string ( fieldset, string )
- vector or list grib_get_long_array ( fieldset, string )
- vector or list grib_get_double_array ( fieldset, string )
These functions return information from the given fieldset’s GRIB header. Available keys (to be passed as the second parameter) can be inspected by Examining the GRIB file (right-click, Examine). Alternatively, use the ecCodes command grib_dump to see the available key names. See GRIB Keys - ecCodes GRIB FAQ for more details on key names.
The first three functions return a number if the input fieldset has a single field, otherwise they return a list of numbers. The
_arrayfunctions return a vector of numbers if the input fieldset has a single field, otherwise they return a list of vectors.The following example shows the retrieval of GRIB header information, including the derived key ‘max’, using the different functions:
print (grib_get_long (data, "editionNumber")) print (grib_get_long (data, "max")) print (grib_get_double (data, "max")) print (grib_get_string (data, "max")) print (grib_get_string (data, "typeOfGrid"))
The output from this on an example single-field GRIB file was:
1 317 317.278808594 317.279 regular_ll
The following example shows how to obtain the list of parallels from a reduced Gaussian grid fieldset:
a = read('/x/y/z/data_in_gg.grb') pl = grib_get_long_array (a, 'pl') print (count(pl)) print (pl)
- fieldset grib_set ( fieldset, list, [string])
This function sets information in the given fieldset’s GRIB header, automatically deducing the type from the value passed (not from the key name). The list provided as the second argument should be a set of key/value pairs.
If the optional third argument is ‘repack’, the data will be repacked . It is required after setting some ecCodes keys (e.g. packingType) involving properties of the packing algorithm. This argument is new in Metview version 5.17.0.
Examples:
f = read("my.grib") f = grib_set(f, ["date", 20150601, # integer "time", 0600, # integer "stepType", "avg", # string "startStep", 0 , # integer "endStep", 31, # integer "longitudeOfLastGridPointInDegrees", 100.5]) # double
# GRIB data with ccsds packing f = read("ccsds.grib") # when we change the packing type repacking must be used f = grib_set(f, ["packingType", "grid_simple"], "repack")
- fieldset grib_set_long ( fieldset, list, [string] )
- fieldset grib_set_double ( fieldset, list, [string])
- fieldset grib_set_string ( fieldset, list, [string])
These functions set information in the given fieldset’s GRIB header, and are type-specific. The list provided as the second argument should be a set of key/value pairs.
If the optional third argument is ‘repack’, the data will be repacked . It is required after setting some ecCodes keys (e.g. packingType) involving properties of the packing algorithm. This argument is new in Metview version 5.17.0.
Example:
data = grib_set_long (data, ["centre", 99, "level", 200])
This function does not modify the input fieldset, but returns a new fieldset with the modifications applied.
Available keys can be inspected by Examining the GRIB file icon in Metview’s user interface (right-click, Examine). Alternatively, use the ecCodes command grib_dump to see the available key names. See GRIB Keys - ecCodes GRIB FAQ for more details on key names.
If applied to a multi-field fieldset, then all fields are modified.
- number gribsetbits ( number )
This function sets the number of GRIB packing bits to the value given (eg 8, 10, 16), and returns the previously used internal value. This function is particularly useful when dealing with 10-bit satellite images as these require GRIB packing to be set to 10 bits.
- fieldset grid_cell_area ( fieldset )
Computes the area of each grid cell in a fieldset with the grid points supposed to be at the centre of the grid cells. The grid cell area is returned in m2 units. This function only works for regular latitude-longitude grids and various types of Gaussian grids.
- fieldset indexes ( fieldset, vector )
Given a fieldset and a vector of target values, this function finds for each gridpoint the indexes of the nearest values in the target. Indexes are zero-based and will always have a minimum value of zero and a maximum value equal to the index of the last element of the target vector. A value lying between two values in the vector will use the index of the nearest value; if equidistant, then the higher value is used. The input vector MUST be sorted in ascending order.
- Example
If these are our inputs:
GRIB: 10,20,30,40 15,25,35,45 8, 4,20,11 VECTOR: | 5,10,15,20,25,30 |then our output would be a new GRIB, with values equal to the input values’ positions in the input vector:
GRIB: 1,3,5,5 2,4,5,5 1,0,3,1
- number or list integral (fieldset)
Computes the surface integral of each field in a fieldset. The result is either a number (for one input field) or a list of numbers (for multiple input fields). The computations are based on the cell area (in m2 units) returned by the grid_cell_area() function.
- number or list integrate ( fieldset )
- number or list integrate ( fieldset,list )
- number or list integrate ( fieldset,fieldset )
This function computes the average of each a field in a fieldset over an area.
If the input fieldset contains only one field, a number is returned. If there is more than one field, a list of numbers is returned. Missing values in the input fieldset are bypassed in this calculation. For each field for which there are no valid values, nil is returned.
If the fieldset is the only argument, the integration is done on all grid points.
If a list is the second argument, it must contain four numbers which are respectively the north, west, south and east boundaries of an area. The integration is done on the grid points contained inside this area:
europe = [75,-12.5,35,42.5] x = integrate(field,europe)
If a fieldset is the second argument it is used as a mask. It should contain either one or as many fields as the first fieldset. If it has a single field then this mask is applied to all fields of the input fieldset. If it has the same number of fields as the input fieldset, then a different mask is applied to each input field. The integration is performed only on the grid points where the mask values are non zero. The following code shows a simple example:
# Retrieve land-sea mask and interpolate to LL grid lsm = retrieve( type : "an", date : -1, param : "lsm", grid : [1.5,1.5], levtype : "sfc" ) # The following line forces the values to 0 or 1. lsm = lsm > 0.5 # Now compute the average value on land and on sea land = integrate(field, lsm) sea = integrate(field, not lsm)
Note
The computations are based on the following approximation of the grid cell areas:
\[A_{i} = 2 R^{2} cos\phi_{i} sin(\frac{\Delta\phi_{i}}{2}) \Delta\lambda_{i}\]where:
R is the radius of the Earth
\(\phi_{i}\) is the latitude of the i-th grid cell
\(\Delta\phi_{i}\) is the size of the grid cells in latitude
\(\Delta\lambda_{i}\) is the size of the i-th grid cell in longitude.
integratethen supposes that \(\Delta\phi_{i}\) is constant and the weighted average over the area is computed as:\[\frac {\sum_{i}f_{i} A_{i}}{\sum_{i}A_{i}} = \frac {\sum_{i}f_{i}cos\phi_{i}\Delta\lambda_{i}}{\sum_{i}cos\phi_{i}\Delta\lambda_{i}}\]The formula above is only used for reduced or regular latitude-longitude and Gaussian grids. For all other grid types
integratesimply returns the mathematical average of the values (just likeaveragedoes).
Warning
Please note that for Gaussian grids the formula can only be only regarded as an approximation since \(\Delta\phi_{i}\) is not constant!
- number or list interpolate ( fieldset,list )
- number or list interpolate ( fieldset,number,number )
Interpolate a fieldset at a given point. The method used is bilinear interpolation. If a list is given, it must contain two numbers - latitude and longitude. If two numbers are given, the first is the latitude, the second the longitude. The field must be a gridded field. If the fieldset has only one field, a number is returned; otherwise a list is returned. Where it is not possible to generate a sensible value due to lack of valid data in the fieldset, nil is returned. Note that a similar function, nearest_gridpoint() , also exists.
- geopoints interpolate ( fieldset,geopoints )
Generates a set of geopoints from a field. The first field of the input fieldset is used. The field is interpolated for each position of the geopoints given as a second parameter. The method used is bilinear interpolation. The output geopoints take their date, time and level from the fieldset. Where it is not possible to generate a sensible value due to lack of valid data in the fieldset, the internal geopoints missing value is used (this value can be checked for with the built-in variable geo_missing_value or removed with the function remove_missing_values). Note that a similar function, nearest_gridpoint() , also exists.
- fieldset laplacian (f: fieldset)
Computes the Laplacian of each field in the fieldset. he computations for a field f are based on the following formula:
\[\triangle f =\frac{1}{R^2 \ cos^2\phi}\frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial \lambda^2} + \frac{1}{R^2}\frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial \phi^2} - \frac{1}{R^2}tan\phi\frac{\partial f}{\partial \phi}\]where:
R: radius of the Earth
\(\phi\): latitude
\(\lambda\): longitude.
The derivatives are computed with a second order finite-difference approximation. The resulting fields contain missing values on the poles. Please note that this function is only implemented for regular latitude-longitude grids.
- vector or list latitudes ( fieldset )
This function returns the grid point latitudes as a vector. If the fieldset contains more than one field it returns a list of vectors. Each of these vectors contains as many elements as grid points in each field.
- vector or list longitudes ( fieldset )
This function returns the grid point longitudes as a vector. If the fieldset contains more than one field it returns a list of vectors. Each of these vectors contains as many elements as grid points in each field.
- fieldset lookup ( fieldset,fieldset )
- fieldset lookup ( fieldset,list )
These two functions build an output fieldset using the values in the first input fieldset as indices in a look-up action on a second input fieldset or input list:
Takes the grid values in the first fieldset and uses them as index in the second fieldset. E.g. a grid value of n in the first fieldset, retrieves the corresponding grid point value of the (n-1)th field of the second fieldset (indexing is 0 based). The output fieldset is built from these values and has as many fields as the first fieldset.
Takes the grid values in the first fieldset and uses them as index in the list - real numbers are truncated, not rounded. E.g. a grid value of n in the first fieldset, retrieves the (n-1)th list element (indexing is 0 based). The output fieldset is built from these values and has as many fields as the first fieldset.
Any missing values in the first fieldset will cause the function to fail with a `value out of range’ error message.
- fieldset mask ( fieldset, list, [string])
For each field of the input fieldset, this function creates a field containing grid point values of 0 or 1 according to whether they are outside or inside a defined geographical area.
The list parameter must contain exactly four numbers representing a geographical area. These numbers should be in the order north, west, south and east (negative values for western and southern coordinates).
If “missing” is specified as the third argument it will change the behaviour so that points outside the area will become missing values and points inside the area retain their original value. New in Metview version 5.13.0.
Non-rectangular masks, and even convex masks can be created by using the operators and , or and not . To create the following mask:
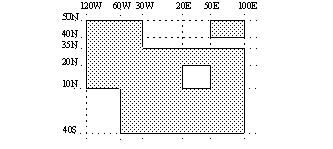
first decompose into basic rectangles:
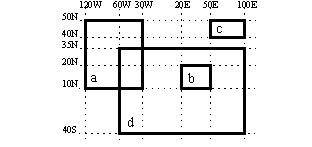
then create a mask for each of them and use and and or to compose the desired mask. This is the corresponding macro:
# Define basic rectangles a = [50,-120,10,-30] b = [20,20,50,10] c = [50,50,40,100] d = [35,-60,-40,100] # The field is used to get the grid information f = retrieve(...) # First compute the union of a,c and d m = mask(f,a) or mask(f,d) or mask(f,c) # Then remove b m = m and not mask(f,b)
The resulting mask field can be used in the integrate() function.
- fieldset max ( fieldset )
- fieldset min ( fieldset )
Returns the fieldset of maximum (minimum) value of the input fieldset at each grid point or spectral coefficient. A missing value in either input fieldset will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset.
- fieldset max ( fieldset,fieldset )
- fieldset min ( fieldset,fieldset )
Returns the fieldset of maximum (minimum) value of the two input fieldsets at each grid point or spectral coefficient. A missing value in either input fieldset will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset.
- fieldset max ( fieldset,number )
- fieldset min ( fieldset,number )
Returns the fieldset of the maximum (minimum) of the number and the fieldset value at each grid point or spectral coefficient. Missing values in the input fieldset are transferred to the output fieldset.
- geopoints max ( fieldset,geopoints )
- geopoints min ( fieldset,geopoints )
Returns geopoints of maximum (minimum) of the fieldset value and the geopoint value at each grid point or spectral coefficient. Missing values, either in the fieldset or in the original geopoints variable, result in a value of geo_missing_value .
- number maxvalue ( fieldset )
- number maxvalue ( fieldset,list )
- number minvalue ( fieldset )
- number minvalue ( fieldset,list )
Returns the maximum (minimum) value of all the values of all the fields of the fieldset. The versions that take a list as a second parameter require a geographical area (north, west, south, east); only points within this area will be included in the calculation. Only non-missing values are considered in the calculation. If there are no valid values, the function returns nil.
- matrix or list matrix ( fieldset )
Generates a matrix containing the values of the input field, or a list of matrices if there are more than one field in the fieldset. Only works with regular lat/long grids.
- fieldset mean ( fieldset, [string] )
Computes the point-wise mean field of a fieldset.
By default a missing value in any field will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset. If the optional second argument is “missing” all the non-missing values across the fields at a given grid point will be used to compute the mean. This option is new in Metview version 5.16.0.
With N fields in the input fieldset by denoting the i-th value in the k-th field by \(f_{i}^{k}\) the output values can be written as:
\[m_{i} = \frac {1}{N} \sum_{k}^{N}f_{i}^{k}\]
- fieldset mean_ew ( fieldset )
Takes a fieldset as its parameter and computes the mean for each line of constant latitude. The result is a fieldset where the value at each point is the mean of all the points at that latitude. Missing values are excluded; if there are no valid values, then the grib missing value indicator will be returned for those points.
- fieldset merge ( fieldset,fieldset,... )
Merge several fieldsets. The same as the operator &. The output is a fieldset with as many fields as the total number of fields in all merged fieldsets. Merging with the value nil does nothing, and is used to initialise when building a fieldset from nothing.
- fieldset ml_to_hl (mfld: fieldset, z: fieldset, zs: fieldset, hlist: list, reflev: string, method: string, [fs_surf: fieldset])
Interpolates a fieldset on model levels (i.e. on hybrid or eta levels used by the IFS) onto height levels (in m) above sea or ground level. At gridpoints where interpolation is not possible missing value is returned. This function has the following positional arguments:
mfld: the fieldset to be interpolated
z: the geopotential fieldset on model levels (it must contain the same levels as mfld but the order of the levels can be different)
zs: the surface geopotential field (if the reflev argument is set to “sea” it should be set to nil).
hlist: the list of target height levels (they can came in any given order)
reflev: specifies the reference level for the target heights. The possible values are “sea” and “ground”
method: specifies the interpolation method. The possible values are “linear” and “log”.
fs_surf: (optional) specifies the field values on the surface. With this it is possible to interpolate to target heights between the surface and the bottom-most model level. If
fs_surfis a number it defines a constant fieldset. Only available whenref_levelis “ground”. New in Metview version 5.14.0.
At gridpoints where the interpolation is not possible a missing value is returned. It can happen when the target height level is below the bottom-most model level or the surface (when
fs_surfis used) or above the top-most level. Please note that model levels we are dealing with in ml_to_hl are “full-levels” and the bottom-most model level does match the surface but it is above it. If you need to interpolate to height levels close to the surface usefs_surf.Note
The actual ECMWF model level definition is stored in the “pv” array in the GRIB message metadata. You can figure out the total number of model levels in the given vertical coordinate system by using the len(pv)/2-1 formula. The typical values are 137 and 91. This can be then used to look up details about actual the model level definitions (e.g. approximate pressure and height values) on this page.
Note
Geopotential is not archived operationally on model levels in MARS at ECMWF. To compute it use
mvl_geopotential_on_ml().The following example shows how to use function
ml_to_hl()together withmvl_geopotential_on_ml():# retrieve the data on model levels - # surface geopotential (zs) is only available in the first forecast step! common_retrieve_params = ( type : "fc", levtype : "ml", step : 12, grid : [1.5,1.5] ) t = retrieve param : "t", levelist : [1, 'to', 137], common_retrieve_params) q = retrieve param : "q", levelist : [1, 'to', 137], common_retrieve_params) lnsp = retrieve( param : "lnsp", levelist : 1, common_retrieve_params) zs = retrieve( param : "z", levelist : 1, type : "fc", levtype : "ml", step : 0, grid : [1.5,1.5]) # compute geopotential on model levels z = mvl_geopotential_on_ml(t, q, lnsp, zs) # interpolate the t field onto a list of height levels above sea level hlevs = [1000, 2000, 3000, 4000, 5000] th = ml_to_hl (t, z, nil, hlevs, "sea", "linear")
- fieldset mod ( fieldset,fieldset )
Returns a fieldset with as many fields as the input fieldsets; the grid point values of the output fieldset are the remainder of the division of the first fieldset by the second fieldset (the function operating field by field). Where the gridpoint values of the second fieldset are larger than those of the first, the output gridpoint value is set to the integer part of the first input gridpoint value. A missing value in either input fieldset will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset. Note that only the integer parts of the inputs are considered in the calculation, meaning that a second parameter of 0.5 would cause a division by zero.
- fieldset mvl_geopotential_on_ml(t:fieldset, q:fieldset, lnsp:fieldset, zs:fieldset)
Computes geopotential on model levels.
All fields must be gridpoint data - no spherical harmonics, and they must all be on the same grid, with the same number of points.
mvl_geopotential_on_mlassumes that there are no other dimensions contained in the data, e.g. all fields should have the same date and time.The return value is a fieldset of geopotential defined on the model levels present in the input data sorted by ascending numeric level order.
The required levels and their ordering in
tandqdepend on the Metview version used:from Metview version 5.14.0:
tandqmust contain the same levels in the same order but there is no restriction on the actual level ordering. The model level range must be contiguous and must include the bottom-most level. E.g. if the current vertical coordinate system has 137 model levels using only a subset of levels between e.g. 137-96 is allowed.in previous Metview versions:
tandqmust contain the full model level range in ascending numeric order. E.g. if the current vertical coordinate system has 137 model levelstandqmust contain all the levels ordered as 1,…, 137.
Note
The actual ECMWF model level definition is stored in the “pv” array in the GRIB message metadata. You can figure out the total number of model levels in the given vertical coordinate system by using the len(pv)/2-1 formula. The typical values are 137 and 91. This can then be used to look up details about actual the model level definitions (e.g. approximate pressure and height values) on this page.
Note
Surface geopotential is defined on model level 1 in MARS at ECMWF. For most recent dates it is available for the 0 forecast step. However, generally it is only available as an analysis field.
The code below illustrates how to use this function:
# retrieves analysis data on model levels r = (date: -1, time: 12, levtype: "ml", grid: [1.5,1.5]) t = retrieve(r,levelist: [1,"to",137],param: "t") q = retrieve(r,levelist: [1,"to",137],param: "q") zs = retrieve(r,levelist: 1,param: "z") lnsp = retrieve(r,levelist: 1,param: "lnsp") # computes the geopotential z_ml = mvl_geopotential_on_ml(t, q, lnsp, zs)
- fieldset mvl_ml2hPa(lnsp: fieldset, mfld: fieldset, plist: list)
Interpolates a fieldset currently on model levels onto pressure levels (in hPa). Locations where interpolation is not possible are returned as missing.
Parameter lnsp is a field of logarithm of surface pressure; mfld is the fieldset to be interpolated and should be on model levels; plist is a list of pressure levels in hPa - the result will be the mfld fieldset interpolated onto these levels. Neither mfld nor plist need to be sorted.
The following code shows a simple example:
# retrieve the data in model levels common_retrieve_params = ( type : "fc", levtype : "ml", step : 12, grid : [1.5,1.5] ) tmod = retrieve param : "t", levelist : [1, 'to', 91], common_retrieve_params) lnsp = retrieve( param : "lnsp", levelist : 1, common_retrieve_params) # interpolate onto a list of pressure levels plevels = [1000, 900, 850, 500, 300, 100, 10, 1, 0.1] tpres = mvl_ml2hPa (lnsp, tmod, plevels)
- number or list nearest_gridpoint ( fieldset,list[,string] )
- number or list nearest_gridpoint ( fieldset,number,number[,string] )
- vector or list nearest_gridpoint ( fieldset,vector,vector[,string] )
Returns the value of the nearest point to a given location (or locations) in each field of a fieldset. The field must be a gridded field. If a list is given, it must contain two numbers - latitude and longitude. If two numbers are given, the first is the latitude, the second the longitude. For batch processing of multiple locations, two vectors can be given, the first is a vector of latitudes, the second the longitudes; this can be much more efficient than multiple calls with a single location each. If the fieldset has only one field, a number (or vector) is returned; otherwise a list of numbers (or a list of vectors) is returned.
By default, when the nearest gridpoint value is a missing value or the location is out of the grid area, nil is returned in the case of a single coordinate, or vector_missing_value in the case of a vector. If an extra parameter ‘valid’ is added to the function call, then of the surrounding points, the nearest valid one is returned; nil will still be returned if all the surrounding points are missing.
Note that a similar function, interpolate(), also exists.
- geopoints nearest_gridpoint ( fieldset,geopoints )
Generates a set of geopoints from a field. The first field of the input fieldset is used. The result is a set of geopoints whose values are those of the nearest gridpoints in the field to the geopoints given as a second parameter. Where it is not possible to generate a sensible value due to lack of valid data in the fieldset, the internal geopoints missing value is used (this value can be checked for with the built-in variable geo_missing_value or removed with the function remove_missing_values). Note that a similar function, interpolate() , also exists.
- list nearest_gridpoint_info ( fieldset,list[,string] )
- list nearest_gridpoint_info ( fieldset,number,number[,string] )
Returns the value and location of the nearest point to a given location in each field of a fieldset. If a list is given, it must contain two numbers - latitude and longitude. If two numbers are given, the first is the latitude, the second the longitude. The field must be a lat-long field. The return value is a list of definitions, one for each field, and each containing the following members: value , latitude , longitude . Where it is not possible to generate a sensible value due to lack of valid data in the fieldset, nil is returned. If an extra parameter ‘valid’ is added to the function call, then of the surrounding points, the nearest valid one is returned; nil will still be returned if all the surrounding points are missing.
The following example illustrates how to use the function.
fs = read (strGribFile) listdef = nearest_gridpoint_info(fs, 51.46, -1.33) loop ngp in listdef print ("Value : ", ngp.value) print ("Latitude : ", ngp.latitude) print ("Longitude : ", ngp.longitude) end loop
- fieldset nobitmap ( fieldset,number )
Returns a copy of the input fieldset (first argument) with all of its missing values replaced with the number specified by the second argument.
Note
See also
bitmap.
- fieldset percentile(...)
Computes the specified percentiles for a given fieldset. This is a Metview icon function, for detailed documentation please see Percentile.
- fieldset poly_mask (fieldset, vector, vector, [string] )
- fieldset poly_mask (fieldset, list, list, [string] )
- fieldset poly_mask (geopoints, vector, vector, [string] )
- fieldset poly_mask (geopoints, list, list, [string] )
New in Metview version 5.16.0.
If the first argument is a
Fieldsetfor each fieldpoly_maskcreates a field containing 0 or 1 values according to whether a grid point is inside (1) or outside (0) the specified polygon(s). If the first argument is aGeopointsa similar operation is performed for all the points in it.The first vector defines the latitudes, while the second one the longitudes of the polygon points. List of vectors can be used to specify multiple polygons; in this case the output mask is generated by forming their union. The polygons are automatically closed up if the first and last coordinates are not the same.
If “missing” is specified as the fourth argument it will change the behaviour so that points outside the area will become missing values and points inside the area retain their original value.
Note
See also
mask,rmask,bitmapandnobitmap.
- fieldset pressure ( fieldset )
- fieldset pressure ( fieldset,number )
- fieldset pressure ( fieldset,list )
- fieldset pressure ( fieldset,fieldset )
This function creates fields of pressure from the logarithm of the surface pressure (lnsp) and a list of model levels. Note that this function only works with gridded fields and assumes that the parameter for lnsp is 152.
The first argument is always a fieldset containing an lnsp field. If no other parameter is given, the list of levels will range from 1 to (number of vertical coordinates/2)-1 as coded in the GRIB header of the lnsp parameter.
The second argument specifies the levels at which the output fields must be generated. To generate a single level, pass a number. For more than one level, either pass a list of levels or a fieldset. If a fieldset is passed as the second parameter, the level information is extracted from each field of the fieldset.
Missing values in the lnsp field are retained in the output fieldset.
Warning
This function is obsolete, use
pressureinstead.
- fieldset rmask ( fieldset,number,number,number )
- fieldset rmask ( fieldset,list )
Similar to mask , except that a round mask is computed with a given radius around a geographical centre point. These can be given by either:
three numbers: latitude, longitude (in degrees), radius (in meters)
a list containing the above three numbers
The name of this function is derived from the fact that it creates a “round mask” or a “radius mask”.
- fieldset rms ( fieldset )
Computes the root mean square of a fieldset. A missing value in any field will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset.
With N fields in the input fieldset by denoting the i-th value in the k-th field by \(x_{i}^{k}\) the output values can be written as:
\[r_{i} = \sqrt {\frac {1}{N} \sum_{k}^{N} (x_{i}^{k})^{2}}\]Note that the following lines are equivalent:
y = rms(x) y = sqrt(mean(x*x))
- fieldset rms_a ( fieldset)
- fieldset rms_a ( fieldset, list )
Computes the area weighted root mean square for each field in the input fieldset. The area, if specified, is a list of numbers representing North, West, South, East. If the area is not specified, the whole field will be used in the calculation. The result is a number for a single field, or a list for a multi-field fieldset.
Note
The computations are implemented via
integrateand the following lines are equivalent:y = rms_a(x) y = sqrt(integrate(x*x))
- fieldset second_derivative_x (f: fieldset)
Computes the second zonal (from West to East) partial derivative of each field in the fieldset. The computations for a field f are based on the following formula:
\[\frac {\partial^2 f}{\partial x^2} = \frac{1}{R^2 \ cos^2\phi}\frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial \lambda^2}\]where:
R is the radius of the Earth in m
\(\phi\) is the latitude
\(\lambda\) is the longitude.
The derivatives are computed with a second order finite-difference approximation. The resulting fields contain missing values on the poles. Please note that this function is only implemented for regular latitude-longitude grids.
- fieldset second_derivative_y (f: fieldset)
Computes the second meridional (from South to North) partial derivative of each field in the fieldset. The computations for a field f are based on the following formula:
\[\frac {\partial^2 f}{\partial y^2} = \frac{1}{R^2}\frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial \phi^2}\]where:
R is the radius of the Earth in m
\(\phi\) is the latitude
The derivatives are computed with a second order finite-difference approximation. The resulting fields contain missing values on the poles. Please note that this function is only implemented for regular latitude-longitude grids.
- fieldset set_values ( fieldset,vector )
- fieldset set_values ( fieldset,list )
- fieldset set_values ( fieldset,vector,string )
- fieldset set_values ( fieldset,list,string )
Creates a new fieldset with all the fields’ values replaced by those supplied. If supplied as a single vector, the values are set in all fields; if a list of vectors is supplied then there must be the same number of vectors as there are fields in the fieldset. The default behaviour is to produce an error if the input fieldset and vector have different numbers of values. If, however, a third parameter (set to the string ‘resize’) is passed to the function, the resulting fieldset will instead be resized to have the same number of values as the input vector - this can be useful when creating a new fieldset from a template. Missing values in the vector(s) are retained as missing values in the fieldset.
- fieldset shear_deformation(fx: fieldset, fy: fieldset)
New in Metview version 5.13.0.
Computes the shear deformation of 2-dimensional vector fields.
The computations for a vector field f=(fx,fy) are based on the following formula:
\[d(f) = \frac{1}{R \ cos\phi}\frac{\partial f_y}{\partial \lambda} + \frac{1}{R}\frac{\partial f_x}{\partial \phi} + \frac{f_x}{R}tan\phi\]where:
R is the radius of the Earth (in m)
\(\phi\) is the latitude
\(\lambda\) is the longitude.
The derivatives are computed with a second order finite-difference approximation. The resulting fields contain missing values on the poles.
Warning
shear_deformationis only implemented for regular latitude-longitude grids.
- fieldset sinlat ( fieldset )
For each field in the input fieldset, this function creates a field where each grid point has the value of the sine of its latitude. For example, the following macro adds the coriolis parameter to each grid point of a field:
# Computes absolute vorticity from vorticity omega = 2 * pi / 86400 coriolis = 2 * omega * sinlat(vort) absvort = vort + coriolis
- fieldset solar_zenith_angle(fs: fieldset, [to_cosine: string])
New in Metview version 5.14.0.
Computes the solar zenith angle for each gridpoint by using the following positional arguments:
fs: input fieldset
to_cosine: (optional) when this argument is specified as set to “to_cosine” the cosine of the solar zenith angle is returned
The result is the solar zenith angle in degrees (unless “to_cosine” is specified when the cosine of the solar zenith angle is returned). The computations are based on the following formula:
\[cos\theta_{s} = sin\phi\, sin\delta + cos\phi\, cos\delta\, cosh\]where:
\(\theta_{s}\) is the solar zenith angle
\(\phi\) is the latitude
\(\delta\) is the declination of the Sun
h is the hour angle in local solar time
The declination of the Sun is computed as:
\[\delta = - arcsin\left(0.39779 cos(0.98565\unicode{xB0} (N+10) + 1.914\unicode{xB0} sin(0.98565\unicode{xB0} (N-2))\right)\]where:
N is the day of the year beginning with N=0 at midnight Universal Time (UT) as January 1. It is a floating point number allowing for fractional days.
A missing value in any field in
fswill result in a missing value in the corresponding grid point in the output fieldset.The dates and times used in the computations are based on the “validityDate” and “validityTime” ecCodes keys. If these are not available for a given field the result will contain missing values for all the gridpoints for that field.
When “to_cosine” is not specified and the GRIB edition of the input field is 2 the ecCodes paramId in the output field is set to 260225 (shortName=”solza”). For GRIB edition 1 this parameter is not defined.
When “to_cosine” is specified the ecCodes paramId in the output is set to 214001 (shortName=”uvcossza”).
- fieldset sort ( fieldset )
- fieldset sort ( fieldset,string )
- fieldset sort ( fieldset,list )
- fieldset sort ( fieldset,string,string )
- fieldset sort ( fieldset,list,string )
- fieldset sort ( fieldset,list,list )
This function accepts a fieldset as input and returns it sorted according to keys and rules specified in the other input arguments.
Specified with only the fieldset as its single argument, sort() sorts in ascending order the fieldset according to the following MARS keys: date, time, step, number (ensemble member), levelist and param (integer ID).
The second argument allows you to modify the precedence of the sorting keys - e.g. if the second argument is a string “param”, then the sorting is done according to the param key. If the second argument is a list you specify a list of sorting keys - e.g. [“param”, “date”] sorts on parameter and then date.
The third argument specifies a sorting direction. This can be a string (“>” or “<”) or a list ([“>”, “<”, “>”,…]). If it is a string, the sorting direction it specifies applies to all sorting keys specified in the second argument. If it is a list, then the second argument must also be a list with the same number of elements - the sorting directions apply to each sorting key specified.
- fieldset speed (u: fieldset, v: fieldset)
Computes the wind speed from the
uandvwind components.The resulting values are speed values in the same units as the input fields. A missing value in either
uorvwill result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset.The ecCodes paramId in the output is set as follows:
10 (atmospheric wind speed)
207 (10m wind speed)
228249 (100m wind speed)
228241 (200m wind speed)
In any other cases the ecCodes paramId is set to 10.
- fieldset stdev ( fieldset )
Computes the standard deviation of a fieldset. A missing value in any field will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset. With N fields in the input fieldset by denoting the i-th value in the k-th field by:math:x_{i}^{k} the output values can be written as:
\[z_{i} = \sqrt {\frac {1}{N} \sum_{k}^{N} (x_{i}^{k})^{2} - (\frac {1}{N} \sum_{k}^{N} x_{i}^{k} )^2}\]Note that the following lines are equivalent:
y = stdev(x) y = sqrt(mean(x*x)-mean(x)*mean(x)) y = sqrt(var(x))
- number or list stdev_a ( fieldset )
- number or list stdev_a ( fieldset,list )
Computes the standard deviation over a weighted area. The area, if specified, is a list of numbers representing North, West, South, East. If the area is not specified, the whole field will be used in the calculation. The result is a number for a single field, or a list for a multi-field fieldset.
- fieldset stretch_deformation(fx: fieldset, fy: fieldset)
New in Metview version 5.13.0.
Computes the stretch deformation of 2-dimensional vector fields.
The computations for a vector field f=(fx,fy) are based on the following formula:
\[d(f) = \frac{1}{R \ cos\phi}\frac{\partial f_x}{\partial \lambda} - \frac{1}{R}\frac{\partial f_y}{\partial \phi} - \frac{f_y}{R}tan\phi\]where:
R is the radius of the Earth (in m)
\(\phi\) is the latitude
\(\lambda\) is the longitude.
The derivatives are computed with a second order finite-difference approximation. The resulting fields contain missing values on the poles.
Warning
stretch_deformationis only implemented for regular latitude-longitude grids.
- fieldset sum ( fieldset )
Computes the point-wise sum of a fieldset. The result is a single-field fieldset.
By default a missing value in any field will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset. If the optional second argument is “missing” all the non-missing values across the fields at a given grid point will be used to compute the sum. This option is new in Metview version 5.16.0.
With N fields in the input fieldset by denoting the i-th value in the k-th field by \(x_{i}^{k}\) the output values can be written as:
\[s_{i} = \sum_{k}^{N} x_{i}^{k}\]
- vector or list surrounding_points_indexes ( fieldset,list[,string] )
- vector or list surrounding_points_indexes ( fieldset,number,number[,string] )
- vector or list surrounding_points_indexes ( fieldset,vector,vector[,string] )
Returns the indexes of the four gridpoints surrounding the given location, ordered by increasing distance from the target point. If a list is given, it must contain two numbers - latitude and longitude. If two numbers are given, the first is the latitude, the second the longitude. The field must be a gridded field. If the fieldset has only one field, a single vector of indexes is returned; otherwise a list of vectors is returned. In the case where the field is a reduced Gaussian grid and the input location is at the North or South pole, beyond the most extreme row of points, there will be a ‘circle’ of surrounding points, and all of these indexes are returned.
For batch processing of multiple locations, two vectors can be given, the first is a vector of latitudes, the second the longitudes; this can be much more efficient than multiple calls with a single location each. If the fieldset has only one field, a single vector is returned; otherwise a list of vectors is returned.
By default, if any of the surrounding points are missing, the function will return nil. To prevent this, and to return all the points regardless, add the option ‘all’ as the last parameter of the function call.
- fieldset tanlat ( fieldset )
For each field in the input fieldset, this function creates a field where each grid point has the value of the tangent of its latitude. The resulting fields contain missing values on the poles.
- fieldset thickness ( fieldset )
- fieldset thickness ( fieldset,number )
- fieldset thickness ( fieldset,list )
- fieldset thickness ( fieldset,fieldset )
This function creates fields of thickness from the logarithm of the surface pressure (lnsp ) and a list of model levels. Note that this function only works with lat/long grids and assumes that the parameter for lnsp is 152.
The first argument is always a fieldset containing an lnsp field. If no other parameter is given, the list of levels will range from 1 to (number of vertical coordinates/2)-1 as coded in the GRIB header of the lnsp .
The second argument specifies the levels at which the output fields must be generated. To generate a single level, pass a number. For more than one level, either pass a list of levels or a fieldset. If a fieldset is passed as the second parameter, the level information is extracted from each field of the fieldset.
Missing values in the lnsp field are retained in the output fieldset.
Warning
This function is obsolete, use
unithicknessinstead.
- fieldset unipressure ( fieldset )
- fieldset unipressure ( fieldset,fieldset )
- fieldset unipressure ( fieldset,list )
- fieldset unipressure ( fieldset,number )
- fieldset unipressure ( fieldset,fieldset,number )
- fieldset unipressure ( fieldset,list,number )
This function creates fields of pressure from the logarithm of the surface pressure (lnsp) and a list of model levels. Unlike pressure() , this function works with all grid types known to Metview (not just lat/long); it also allows the user to override the parameter number for lnsp (default 152).
the first argument is always a fieldset containing an lnsp field. If no other parameter is given, then pressure is computed for all model levels that are described in the GRIB header of fieldset .
if number is given (always the last parameter) it is the lnsp parameter code (default is 152).
list should contain model levels for which pressure is to be computed. Note that also for a single model level one has to use a list (this is a signature difference compared to the old function pressure() ).
if fieldset is given as the second parameter then pressure is computed for those model levels found in the second fieldset.
Missing values in the lnsp field are retained in the output fieldset.
- fieldset unithickness ( fieldset )
- fieldset unithickness ( fieldset,fieldset )
- fieldset unithickness ( fieldset,list )
- fieldset unithickness ( fieldset,number )
- fieldset unithickness ( fieldset,fieldset,number )
- fieldset unithickness ( fieldset,list,number )
This function creates fields of thickness from the logarithm of the surface pressure (lnsp) and a list of model levels. Unlike thickness() , this function works with all grid types known to Metview (not just lat/long); it also allows the user to override the parameter number for lnsp (default 152).
the first argument is always a fieldset containing an lnsp field. If no other parameter is given, then thickness is computed for all model levels that are described in the GRIB header of fieldset .
if number is given (always the last parameter) it is the lnsp parameter code (default is 152).
list should contain model levels for which thickness is to be computed. Note that also for a single model level one has to use a list (this is a signature difference compared to the old function thickness() ).
if fieldset is given as the second parameter then thickness is computed for those model levels found in the second fieldset.
Missing values in the lnsp field are retained in the output fieldset.
- univertint(fs: fieldset[, lnsp_code: number])
- univertint(lnsp: fieldset, fs: fieldset[, levels: list])
Performs a vertical integration for pressure levels or ECMWF (hybrid) model levels using the following positional arguments:
fs: input fieldset
lnsp: lnsp fieldset defined on model level 1
lnsp_code: ecCodes paramId for lnsp
levels: level range as a list of [top, bottom]
The function has to be called in a different way depending on the type of vertical levels in
fs:Pressure levels: the function has to be called with the
fsargument only.Model levels:
when no
lnspis specifiedfsmust also contain an lnsp field. In this case the optionallnsp_codecan specify the ecCodes paramId used to identify the lnsp field (by default the value of 152 is used.when
lnspis specified it defines the lnsp field.the optional
levelsparameter is a list with two numbers [top, bottom] to specify the level range for the integration. Iflevelsis not specified the vertical integration is performed for all the model levels infs.
A missing value in any field will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset.
Computations
The computations are based on the following formula:
\[\int_{p_{top}}^{p_{bottom}} f \frac{dp}{g}\]where:
f: input fieldset
p: pressure
g: acceleration of gravity (9.80665 m/s2).
The actual algorithm is slightly different on pressure and model levels.
For pressure levels the data is first sorted by pressure in ascending numerical order resulting in \(f_{i}\) fields on levels \(p_{i}\) i=0,…,N (with \(p_{i+1} > p_{i}\)). Then, to estimate the pressure differential we form N layers by using the pressures halfway between two levels. If we denote the halfway pressure between level i and i+1 by \(p^{*}_{i}\) we can write the layer sizes as follows:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}\Delta p_{0} = p^{*}_{0} - p_{0}\\\Delta p_{i} = p{*}_{i+1} - p^{*}_{i}\\\Delta p_{N} = p_{N} - p^{*}_{N-1}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]and estimate the integral like this:
\[\sum_{i=0}^{N} f_{i} \frac{\Delta p_{i}}{g}\]For model level data the vertical coordinate system definition is stored in the “pv” array in the GRIB header. A model level is defined on a “full level”, which lies in the layer between the two neighbouring “half levels”. Using
lnspand the “pv” array we can determine the \(\Delta p_{i}\) layer size for each level individually. The integral is then estimated in the same way as was shown above for pressure levels. Please note that you can useunithicknessto compute the layer sizes (the “thickness” in the function name actually means “layer size”). For more details about the model level definitions please visit this page.- Example
# Retrieve cloud liquid water content clwc = retrieve( levtype : "ml", levelist : [1,"to",137], param : "clwc", date : -1, grid : [2,2] ) # Retrieve lnsp lnsp = retrieve( levtype : "ml", levelist : 1, param : "lnsp", date : -1, grid : [2,2] ) # Compute total amount of liquid water r = univertint(lnsp,clwc)
- date or list valid_date ( fieldset )
Returns the valid dates (including the time components) of the given fields. If the fieldset has only one field, a date is returned; otherwise a list of dates is returned.
- vector or list values ( fieldset )
This function returns the grid point values as a vector. If the fieldset contains more than one field it returns a list of vectors. Each of these vectors contains as many elements as grid points in each field. Missing values are included in the results as vector_missing_value.
# x is a fieldset of n fields xgrid = values(x) field1_values = xgrid[1] gridpoint1 = field1_values[1] # or equivalently gridpoint1 = xgrid[1][1]
- fieldset var ( fieldset )
Computes the variance of a fieldset. A missing value in any field will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset. With n fields in the input fieldset by denoting the i-th value in the k-th field by \(x_{i}^{k}\) the output values can be written as:
\[v_{i} = \frac {1}{n} \sum_{k}^{n} (x_{i}^{k})^2 - \frac {1}{n} (\sum_{k}^{n} x_{i}^{k})^2\]Note that the following lines are equivalent:
y = var(x) y = mean(x*x)-mean(x)*mean(x)
- number or list var_a ( fieldset )
- number or list var_a ( fieldset,list )
Computes the variance over a weighted area. The area, if specified, is a list of numbers representing North, West, South, East. If the area is not specified, the whole field will be used in the calculation. The result is a number for a single field, or a list for a multi-field fieldset.
- fieldset vertint ( fieldset )
- fieldset vertint ( fieldset,fieldset )
This function performs a vertical integration of the input fieldset, which must contain a range of model levels for the same parameter. A missing value in any field will result in a missing value in the corresponding place in the output fieldset. If the function is called with the fieldset as its single argument, it must also contain the logarithm of the surface pressure (lnsp ). If the function is called with two parameters, the first one is a fieldset containing an lnsp field, the second one is the multi-level fieldset.
The computations are based on the following formula:
\[\int_{p_{top}}^{p_{bottom}} f \frac{dp}{g}\]where:
f: input fieldset
p: pressure
g: acceleration of gravity (9.80665 m/s2).
Warning
This function is obsolete, use
univertintinstead.
- fieldset vorticity (fx: fieldset, fy: fieldset)
Computes the vertical component of the curl differential operator for 2-dimensional vector fields. For wind fields (i.e. when the input fieldsets are u and v wind components) this computes the relative vorticity (ζ). The computations for a vector field f=(fx,fy) are based on the following formula:
\[\zeta =\frac{1}{R \ cos\phi}\frac{\partial f_y}{\partial \lambda} - \frac{1}{R}\frac{\partial f_x}{\partial \phi} + \frac{f_x}{R}tan\phi\]where:
R is the radius of the Earth (in m)
\(\phi\) is the latitude
\(\lambda\) is the longitude
The derivatives are computed with a second order finite-difference approximation. The resulting fields contain missing values on the poles. If the input fields are horizontal wind components the GRIB paramId of the resulting field is set to 138 (relative vorticity). Please note that this function is only implemented for regular latitude-longitude grids.
- number w_from_omega(omega: number, t: number, p: number)
- vector w_from_omega(omega: vector, t: vector, p: vector)
- fieldset w_from_omega(omega: fieldset, t: fieldset)
- fieldset w_from_omega(omega: fieldset, t: fieldset, p: fieldset)
Computes the hydrostatic vertical velocity from pressure velocity (omega) for a given temperature and pressure, where
omega: pressure velocity (Pa/s)
t: temperature (K)
p: pressure (Pa)
The result is the vertical velocity in m/s units. On error nil is returned. The following rules are applied when omega is a fieldset:
if omega is a pressure level fieldset no pressure argument is needed
if omega is defined on ECMWF model levels (hybrid/eta) p is either a single LNSP (logarithm of surface pressure, identified by paramId=152) field or a fieldset defining the pressure on the levels of omega
for other level types p is a fieldset defining the pressure on the levels of omega
The computation is based on the following hydrostatic formula:
\[w = - \frac{\omega T R_{d}}{p g}\]where
Rd is the specific gas constant for dry air (287.058 J/(kg K)).
g is the gravitational acceleration (9.81 m/s2)
This functions was introduced in version 5.10.0.
- list of numbers xy_from_polar(magnitude: number, dir: number)
- list of vectors xy_from_polar(magnitude: vector, dir: vector)
- fieldset xy_from_polar(magnitue: fieldset, dir: fieldset)
Converts vector data from meteorological polar representation to xy representation. In polar representation the data is specified by two components:
magnitude: represents the speed/magnitude
dir: represents the direction of the vector in degrees. Angles measured from South in clockwise direction.
In the target xy representation the x axis points East while the y axis points North.
The type of the result depends on the type of the input data
if the input is number the result is a list of two numbers
if the input is vector the result is a list of two vectors, the first vector contains the x components while the second vector the y components
if the input is fieldset the result is a fieldset where an x component field is immediately followed by the corresponding y component field.
New in Metview 5.10.0*